Introduction to AI Revolution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept confined to sci-fi movies; it is an evolving technology revolutionizing industries and daily life. At the heart of this transformation are Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), two powerful branches of AI enabling machines to learn from data and make intelligent decisions, as shown in Figure 1. These technologies power recommendation engines, voice assistants, autonomous vehicles, and even medical diagnostics.
This article explores how ML and DL are shaping industries, their core mechanisms, and their future implications in an AI-driven world.
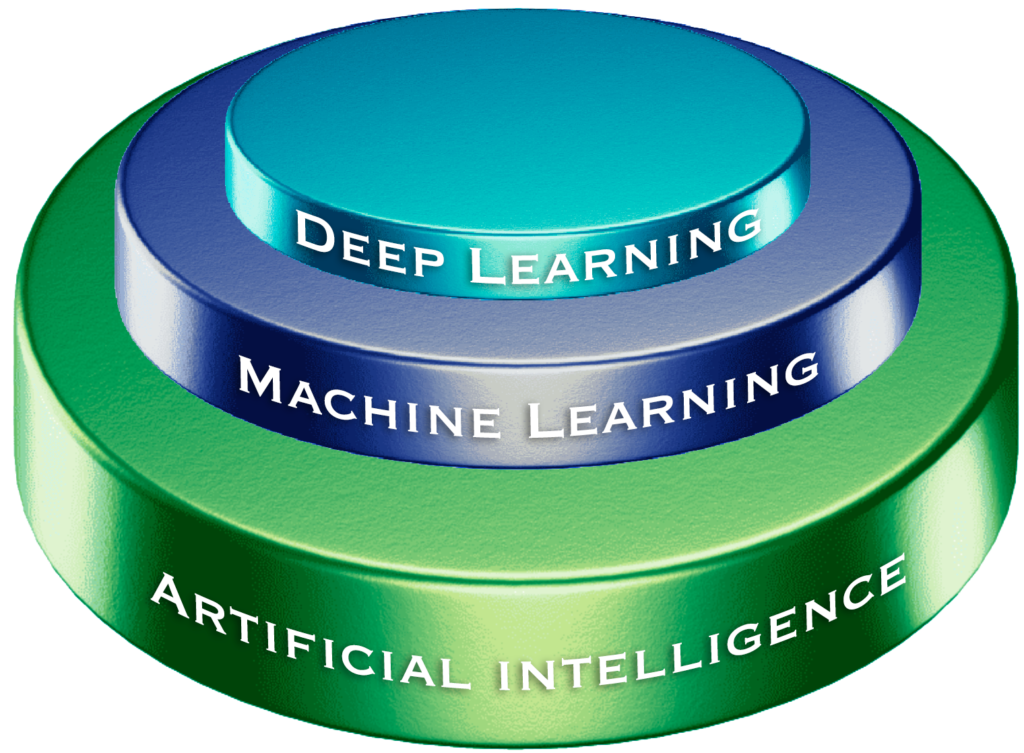
Figure 1
Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is a broad field focused on developing intelligent systems capable of performing human-like tasks such as problem solving, speech recognition, and decision-making.
There are two primary types of AI:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Designed for a specific task (e.g., Alexa, recommendation algorithms).
- General AI (Strong AI): Hypothetical AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can do.
AI’s progression is fueled by ML and DL, allowing machines to analyze vast amounts of data and continuously improve their performance.
Machine Learning (ML) Basics
Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on training algorithms to recognize patterns and make decisions without explicit programming. Unlike traditional programming, where rules are manually coded, ML algorithms learn from data and improve over time, as shown in Figure 2.
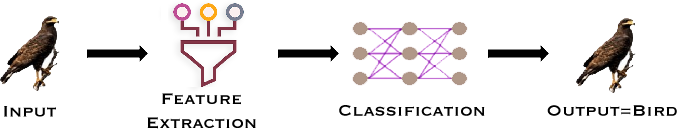
Figure 2
ML models are categorized into three main types:
- Supervised Learning: The model is trained on labeled data, where each input has a known output.
- Example: Spam detection in emails, image recognition.
- Unsupervised Learning: The model is given unlabeled data and must identify patterns.
- Example: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): An AI agent learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties.
- Example: Robotics, self-driving cars, game AI (AlphaGo).
📌 Key applications of Machine Learning
- Fraud detection
- Predictive analytics and recommendation systems (Netflix, Amazon).
Deep Learning (DL) Explained
Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers (“deep” networks) to process and analyze data. These neural networks mimic the human brain, learning complex patterns through layers of artificial neurons, as shown in Figure 3.
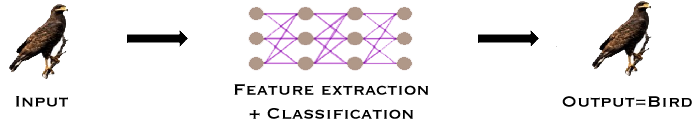
Figure 3
🔹 Why is Deep Learning powerful?
- Specializes at analyzing large, unstructured data (images, speech, text).
- Powers breakthroughs in computer vision, speech recognition, and NLP.
📌 Key Applications of Deep Learning
- Computer Vision: Recognizing objects, faces, and movements in images and videos.
- Used in autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and security systems.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Machines understanding and generating human language.
- Used in chatbots, machine translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Speech Recognition: Transcribing and understanding spoken words.
- Used in voice assistants (Siri, Alexa) and call center automation.
Impact of ML and DL Across Industries
ML and DL are driving innovation across various industries:
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostics, personalized treatments, drug discovery.
- Finance: Fraud detection, automated trading, credit risk assessment.
- Retail: AI-driven recommendation engines, inventory management.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, defect detection using image recognition.
Challenges and Limitations of ML and DL
Despite their potential, ML and DL face key challenges:
- Data Privacy Issues: AI models rely on large datasets, raising privacy concerns.
- Algorithmic Bias: Bias in training data leads to unfair AI decisions.
- High Computational Costs: Training deep learning models requires powerful GPUs and cloud computing.
FAQs
- What is the difference between ML and DL?
- ML requires manual feature extraction, while DL automatically extracts features using neural networks.
- Can AI replace human jobs?
- AI will automate some jobs but also create new AI-driven careers.
- How does reinforcement learning work?
- It uses rewards and penalties to train an agent to make decisions.
- What industries use AI the most?
- Healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing are major AI adopters.
- Is deep learning only used for image recognition?
- No, it is also used in NLP, speech recognition, and recommendation systems.